Hepato Biliary & Pancreatic Surgery
UNIQUE FEATURES
Advanced expertise in stents, ERCP, spyglass cholangioscopy and pancreatic cyst drainage
Laparoscopic necrosectomy done for necrotic pancreatitis
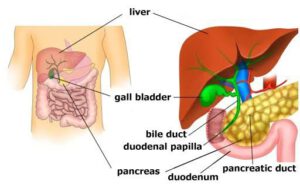
This specialty mainly focuses on surgical problems of the liver, pancreas, and bile duct, mostly chronic pancreatitis, acute necrotizing pancreatitis, pseudocyst of the pancreas, hepatic cysts, choledochal cyst, bile duct strictures, periampullary malignancy, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic tumours, gallbladder cancer, and bile duct cancer.
Usually, patients present to a HBP surgeon to evaluate progressive jaundice, which is the yellowish discolouration of eyes, nail beds, solid tumours in the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and evaluation of abdominal pain due to chronic pancreatitis, and acute severe necrotizing pancreatitis.
Our team of transplant surgeons function 24/7 for the wellbeing of our patients. We have performed numerous hepatectomies, hepatic cyst excisions, radical hepatectomies, Whipple’s surgery, distal pancreatectomy, cysto-gastrostomy, lateral pancreaticojejunostomy, Frey’s procedure, and hepaticojejunostomy.
Advanced expertise in stents, ERCP, spyglass cholangioscopy and pancreatic cyst drainage
Laparoscopic necrosectomy done for necrotic pancreatitis
HEPATO-BILIARY-PANCREATIC SURGERY FAQ
Hemolytic anaemia – malaria, sickle cell anaemia, immune and non-immune causes ⮚ Hepatic causes
Acute hepatitis – HAV, HBV, HCV infections
Sepsis
Hepatotoxicity secondary to drug overdose
Hepatocellular carcinoma
⮚ Post-hepatic causes
o Acute cholangitis o Acute cholecystitis o Blockage of the bile duct due to stone or mass o Duodenal, pancreatic, or biliary duct cancers